Companies can achieve unprecedented levels of operational efficiency and optimize operations through the fusion of traditional forecasting practices with AI technology. This also helps anticipating customer demand, strategic decision-making, and customer-centricity. This synergy enables businesses to adapt swiftly to market dynamics. Also, leverages predictive insights for resource allocation. Ultimately enhance their competitiveness.
What is Demand Forecasting?
The process that can bring significant benefits to a business is called Demand forecasting. It is an essential process for every manufacturing company. It plays a crucial role. By predicting customer demand accurately, companies can allocate resources effectively. It enables companies measure their performance. Develop strategies to exploit opportunities. Increase their market share.
The process of demand forecasting involves estimating customer demand for a product based on historical sales data. Other relevant factors are also considered. Creating a demand forecast helps companies better understand and predict their product demand. It enables informed business decisions making. By having a clear demand plan, companies can ensure they have the right amount of product supply to meet their customers’ needs.
Demand forecasting is a critical aspect of supply chain management. It informs various downstream processes such as procurement, purchasing, logistics, and distribution. Having an accurate demand forecast works as a catalyst for companies in planning their supply chain operations. They become more effective resulting in better customer satisfaction. Increased profitability is what can be achieved easily.
The importance of demand forecasting
Demand forecasting is an indispensable element of business planning. It enables companies to predict future demand. Examining both internal and external data. By determining how much supply should be produced to meet the projected demand improves decision making. Internal data such as historical data can be used to identify trends. Patterns in demand. Whereas external data such as weather, seasonal variations, and supply chain constraints can be used to further refine the forecast. By doing so, companies can ensure that they produce enough supply to fulfill customer demand. They can avoid potential supply chain disruptions. Potentially gain a competitive edge in the market.
For example, let’s say a food manufacturer is planning to launch a new product. They want to determine the potential demand for the product in the market. They can use demand forecasting techniques to predict the future demand for the product. Based on historical data, market trends, and other external factors such as the current economic situation, consumer preferences, and marketing efforts. By analyzing this data, the demand planners can estimate the demand for the new product. This helps company decide how much supply they need to produce. This also aids company make informed decisions about pricing, marketing, and distribution strategies. For example, if the demand forecast for the new product is high, the company might choose to invest more in marketing efforts to capitalize. In case the forecast is low, the company might decide to delay the launch. Or reduce the production to avoid potential waste and losses. In this way, demand forecasting contributes in affecting their profitability, market share, and overall success in the market.
Key Factors in Demand Forecasting
Factors Influencing the Demand Forecasting Process Forecasting demand is a complex endeavor. This involves collecting data, analyzing trends, and making informed assumptions about future market forces. Despite the advancements in data analytics and forecasting techniques, several factors can significantly impact the accuracy of demand forecasts.
Data Quality: Securing precise and comprehensive data for forecasting is often a challenge. While historical sales data provides valuable insights, it may not fully reflect evolving market dynamics and changing consumer behaviors. Moreover, predicting the preferences of potential future customers remains inherently uncertain.
Access to Target Customers: Obtaining insights from prospective customers through market research, surveys, and focus groups is essential for understanding shifting consumer preferences. However, engaging target customers can be demanding, especially in industries where time constraints or limited interest impede the research process. For instance, reaching out to busy medical professionals for feedback on innovative products can be particularly challenging.
Complexity of Underlying Forces: Interpreting data involves identifying patterns and trends. This is due to underlying market forces. Developing accurate demand forecasts requires modeling these forces. This happens within the constraints of simplified methodologies. Failure to account for nuances in demand patterns, such as irregular growth or seasonal fluctuations, can lead to forecast inaccuracies, especially over extended forecasting horizons.
Uncertainties in Future Conditions: Forecasting future demand entails inherent uncertainties even with detailed data analysis and robust modeling.
Assumptions made based on current market conditions and historical trends may not hold true in the face of unforeseen events or disruptions. Factors like new competitors, unexpected market trends, or global incidents can swiftly alter demand trajectories, challenging the reliability of long-term forecasts.
Navigating these factors is crucial for enhancing the precision and reliability of demand forecasts, enabling businesses to adapt to changing market landscapes and make informed strategic decisions.
The Systematic Process of Demand Forecasting for Optimal Business Operations
Demand forecasting operates through a structured methodology. Initially, planners generate a forecast employing statistical or calculated techniques. This initial forecast acts as a foundation, which is then enriched with inputs from various departments such as Sales, Marketing, Product Management, and Finance. These inputs contribute to a more comprehensive and refined consensus forecast.
To construct an accurate demand forecast, planners compile transactional data and align it with the dimensions, hierarchies, levels, and attributes that represent the organizational structure. This data, often extensive, is managed within specialized software that employs calculations, time series models, or machine learning technology to generate the forecast. Subsequently, planners analyze and visualize this forecast, using exception management to identify and resolve any discrepancies or anomalies.
Challenges in demand forecasting may encompass managing product life cycles, including new product introductions, transitions, and end-of-life dates, as well as addressing forecast accuracy, bias, and outliers. Planners employ techniques such as tournaments, scenario analyses, and simulations to compare forecasts, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments through forecast overrides.
The refined demand forecast undergoes assessment in Demand Reviews, where collaborative discussions with Sales and Marketing occur. This collaborative effort aims to address any gaps in the forecast relative to budget constraints and capitalize on market share opportunities. Strategies such as events, promotions, and pricing adjustments are considered to align the forecast with business objectives.
Ultimately, a consensus forecast is finalized, authorized, and integrated into the monthly Sales and Operations Planning meeting. This forecast serves as a key input for Supply Planning, guiding decisions related to purchasing, manufacturing, and delivery planning. By following this systematic process, businesses can optimize their operations and ensure alignment between supply chain activities and customer demand.
Types of demand forecasting
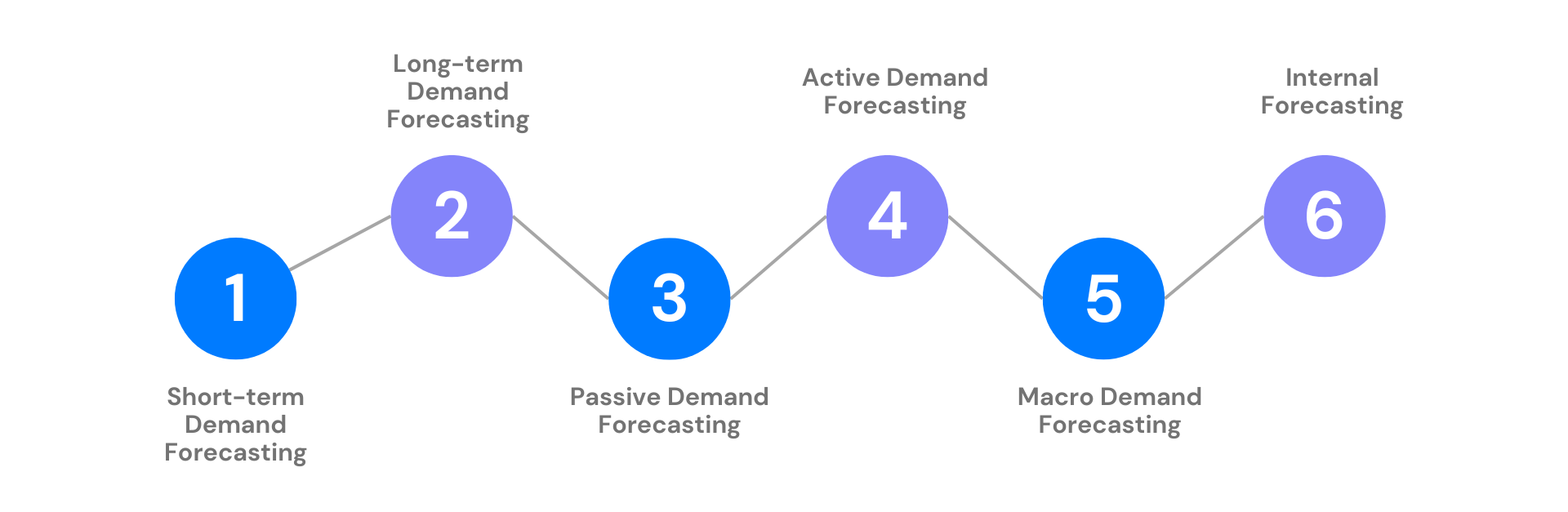
Short-term Demand Forecasting
- Methods: Utilizes techniques like time series analysis, moving averages, and exponential smoothing to project demand in the near future.
- Applications: Facilitates inventory management, production scheduling, and logistics planning, ensuring timely response to demand fluctuations and minimizing stockouts or overstock situations.
Long-term Demand Forecasting
- Approaches: Employs strategic planning tools such as trend analysis, market research, and scenario planning to forecast demand over an extended period.
- Benefits: Helps in long-term capacity planning, resource allocation, and investment decisions, enabling businesses to align their growth strategies with anticipated market demands.
Passive Demand Forecasting
- Usage: Suitable for stable markets or products with consistent demand patterns, leveraging historical data to predict future trends.
- Advantages: Provides a baseline forecast for operational stability, aids in budgeting and resource allocation, and supports risk management by identifying potential deviations from historical norms.
Active Demand Forecasting
- Factors Considered: Incorporates market intelligence, competitor analysis, and economic indicators to forecast demand in dynamic and evolving market conditions.
- Value: Enables businesses to capitalize on growth opportunities, launch targeted marketing campaigns, introduce new products, and adapt strategies in response to market dynamics.
Macro Demand Forecasting
- Scope: Considers external factors such as GDP trends, industry forecasts, geopolitical events, and regulatory changes that influence overall market demand.
- Strategic Guidance: Guides strategic decision-making at a macroeconomic level, helping businesses align their operations with broader economic trends and mitigate risks associated with external disruptions.
Internal Forecasting
- Data Sources: Utilizes internal data sources such as sales records, customer feedback, and operational metrics to forecast demand based on organizational performance.
- Insights: Provides valuable insights into consumer preferences, operational efficiencies, and areas for improvement, supporting data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement initiatives.
These additional details highlight the diverse approaches and applications of each type of demand forecasting, emphasizing their importance in optimizing business operations, enhancing competitiveness, and driving sustainable growth.
Demand forecasting for your business
Demand forecasting plays a crucial role for businesses as it aids in predicting future demand, enabling effective capacity planning and inventory management to ensure a balance between supply and demand in different regions and channels. This process becomes fundamental for businesses to avoid stockouts or surplus inventory, ultimately leading to operational efficiency and improved customer satisfaction.
Qritrim offers specialized assistance in demand forecasting through its AI-driven solutions. By utilizing customized AI models that are designed to interpret and analyze domain-specific data, businesses can benefit from accurate predictions tailored to their unique circumstances. Through enhanced decision-making processes based on deep domain-specific insights and continuous learning from new data, Qritrim enables companies to make informed choices regarding capacity planning and inventory management. The advanced capabilities of the Qi platform, such as real-time data processing, scalable AI model development, and no-code/low-code interfaces, empower businesses to optimize their supply chains and effectively meet demand fluctuations across various regions and channels.